Pregnancy: the belly is quite heavy, not the legs!
Compression, the forgotten part of pregnancy
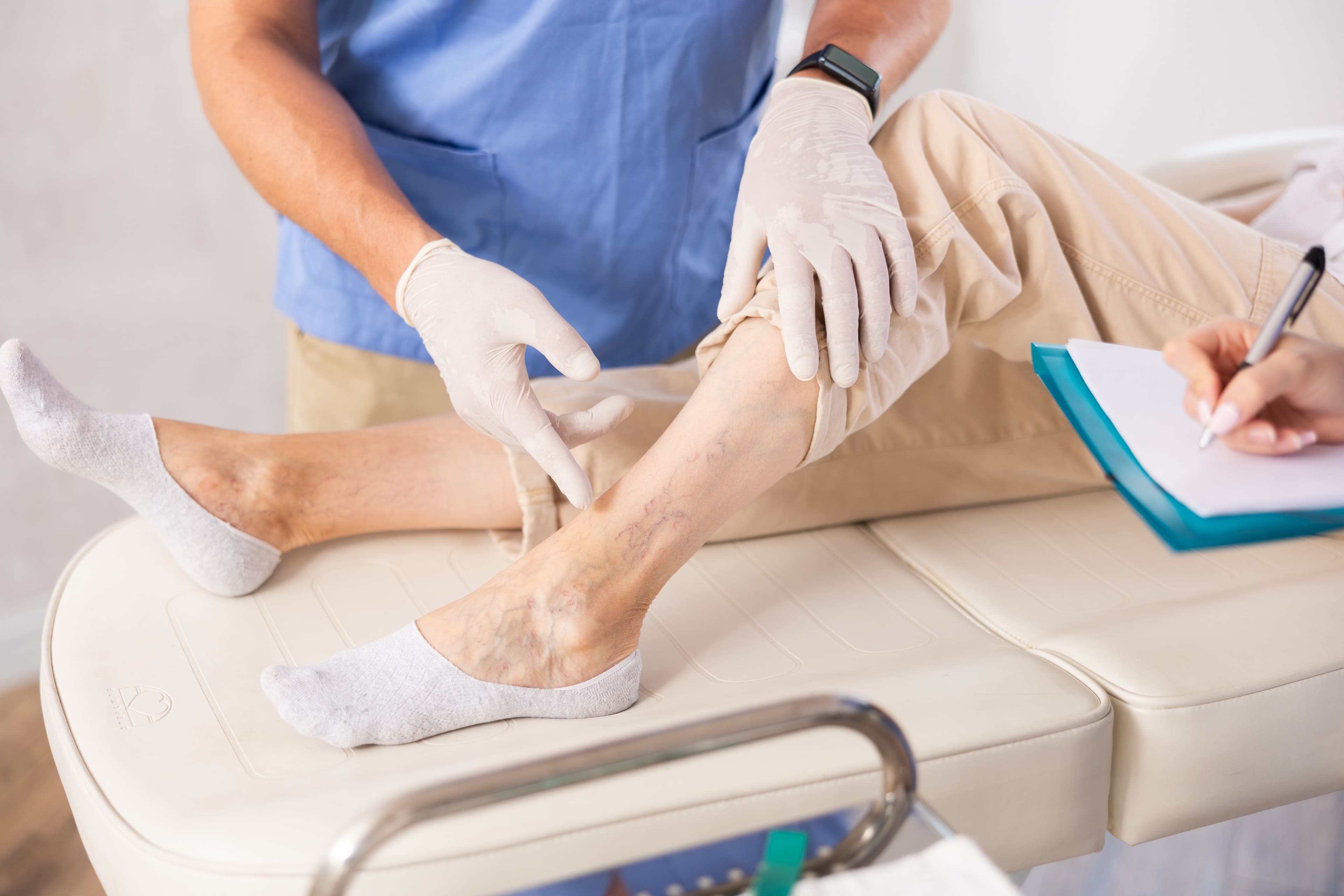
Although a magical time, pregnancy represents a key change in the lives of all pregnant women, who have to deal with physical and hormonal changes. An aspect of pregnancy that is often forgotten or little mentioned is the appearance of signs of venous insufficiency such as heavy legs, leg edema or varicose veins.
Venous insufficiency results in poor venous return. The blood circulating in the veins of the lower limbs has difficulty going back to the heart. Pregnancy, with the increase in hormones, can aggravate or cause the appearance of venous insufficiency, especially in the case of multiple pregnancies or repeated pregnancies(1).
Compression thus plays a key role in the support of future mothers. With tapering compression on the leg, compression products, which are commonly referred to as compression, will put pressure on the veins, promoting blood flow and venous return to the heart, reducing the risk of heavy legs, swelling and varicose veins.
Why is it important to wear compression socks or tights during pregnancy?
While hormones, especially estrogen and progesterone, play a major role in venous insufficiency during pregnancy, there are also mechanical reasons for these predispositions(1). The more the pregnancy progresses, the larger the uterus becomes and the blood vessels in the lower limbs and pelvis compress. Also, during pregnancy, the mother's blood volume increases because the placenta is rich in blood and blood vessels. Blood stagnation can then occur in the legs, dilating the veins and revealing varicose veins(2). During pregnancy, 1 in 2 women will see the appearance of varicose veins(1).
The venous hypertension caused by this stagnation of blood in the lower limbs causes the outflow and accumulation of fluid, lymph, outside the vessels, which can create edema(2).
Finally, a tendency to be hypercoagulable, i.e. to form blood clots inappropriately, occurs during pregnancy as a result of various mechanisms impacting coagulation factors, which can increase the risk of thromboembolic events(1) such as phlebitis. Wearing compression reduces these risks.
Did you know? A pregnant woman is 5x more exposed to venous thromboembolic disease than a woman of the same age who is not pregnant; The risk nevertheless remains low (1/1,000)(1). It is therefore essential for pregnant women to wear compression from the first month of pregnancy until postpartum(4). The French National Authority for Health (HAS) advises that it should be continued for six weeks after natural delivery and six months after a caesarean section(4).
On a lighter note, it is not uncommon for a pregnant woman to experience dizziness during her pregnancy(3). Wearing compression is also recommended to help with orthostatic hypotension, the drop in blood pressure when moving from lying down to standing.
How to take care of your legs with VENOFLEX
The compression must be put on when you wake up: the tight knit is then easier to put on because the legs and ankles have not yet swollen. It will have to be kept on all day.
The VENOFLEX Maternity range meets the needs of pregnant women to accompany them throughout these nine months.
- Aurore Blin, Venous insufficiency, Pharmaceutical News, Volume 62, Issue 622, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpha.2022.11.014.
- Pregnancy and venous insufficiency - VIDAL. (n.d.). VIDAL. https://www.vidal.fr/maladies/coeur-circulation-veines/jambes-lourdes/grossesse.html#:~:text=Sa%20compression%20g%C3%AAne%20ce%20retour,lorsque%20la%20pression%20sanguine%20augmente
- Bánhidy, F., Ács, N., Puhó, E. et al. Hypotension in pregnant women: a population-based case–control study of pregnancy complications and birth outcomes. Hypertens Res 34, 55–61 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2010.172
- Medical compression for the prevention of venous thrombosis - GOALS sheet. (n.d.). Haute Autorité de Santé. https://www.has-sante.fr/jcms/r_1437992/fr/la-compression-medicale-en-prevention-de-la-thrombose-veineuse-fiche-buts
- Market study conducted in France with 200 patients – POTLOC – May 2023.
- Use of a yarn that gives it great elasticity.
- An entry-level range of products generally practiced without exceeding on the French market.
- Flax fiber with thermoregulatory properties, http://news.europeanflax.com/fr/lin/beneficeslin/ European linen - the creative and innovative green fibre of the future, CELC MASTERS OF LINEN
- Socks that stretch in height and width.
- https://www.la-federation.com/data/club-maille_58014/fiche/108/leaflet_fibres_synthetique_fr_080d5.pdf.
- Techni'sens EH2798 study for Thuasne® - February 2019. Ease of fitting and removal, comfort, softness and purchase intention for the Thuasne® Soft &Care class 3 product vs Sigvaris. Expert, Varisma Confort coton, Legger, Radiante 93 Coton and Varisan Elle & Lui, on 66 patients. Our overall rating of7,66/10 after use, is significantly higher than other products tested. 71% purchase intention.
The products mentioned are class I medical devices intended for the treatment of venous pathologies. These medical devices are regulated health products that bear, under this regulation, the CE marking. Indications and contraindications: refer to the package leaflets. Read the instructions for use, indications and contraindications of the products carefully. If in doubt, consult a healthcare professional.