Osteoarthritis of the knee affects younger adults too!
So while OA of the knee is mainly associated with age, young adults can also be affected, especially if they engage in intensive sports activities(3). It is estimated that one in ten 40-year-olds may suffer from osteoarthritis of the knee!(4)
The causes of osteoarthritis in young adults
Arthritic joint deterioration in young people is generally caused by repeated high impacts(3). These impacts are often encountered in intensive sports, such as football, Tennis or contact sports5. Repeated injuries resulting from sports activities increase the risks of developing osteoarthritis of the knee.
But sport isn’t always the culprit! In fact, more than 50% of cases of osteoarthritis may be associated with a genetic predisposition(6). In addition, young people who are overweight or obese are known to be at greater risk of developing osteoarthritis, due to the excessive stress on their joints(7).
Symptoms to watch out for if you are a young adult
Young adults, especially athletes, often have a higher tolerance to pain, which can significantly delay diagnosis(3).
Therefore it is important to watch out for symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee. The most common symptoms are: localised pain in the knee, a reduced range of motion, joint stiffness and cracking noises(3).
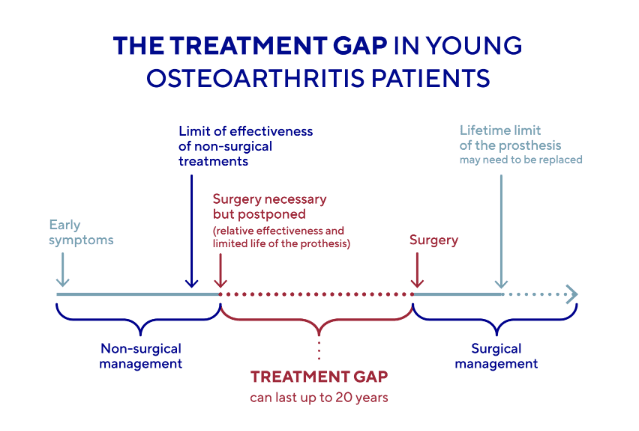
A 20-year treatment gap
Young, active patients with osteoarthritis of the knee pose a challenge when it comes to managing their condition. That’s because the effectiveness of nonsurgical treatments (painkillers and physical exercise) does not enable the progression of this degenerative disease to be halted in the long term. In addition, the surgical options are invasive, have only a relative efficacy and a limited life span, and can also have significant side effects(8).
The time between the exhaustion of non-surgical treatments and the start of surgical treatment is defined in the literature as a “treatment gap”. The great majority of patients under the age of 60 with early to moderate OA of the knee fall into this gap at some point or another.
In total, almost 20% of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee are living in a “treatment gap”, which lasts for an average of almost 20 years! Research on the subject concludes that there is a crucial need for new treatment options that are more effective, safer, and better accepted by these patients(9).
If you have any questions, ask your doctor for advice.
- Heidari, B. (2011, 1 janvier). Knee osteoarthritis prevalence, risk factors, pathogenesis and features : Part I. PubMed Central (PMC). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3766936/
- Long, H., Liu, Q., Yin, H., Wang, K., Diao, N., Zhang, Y., Lin, J., & Guo, A. (2022e). Prevalence Trends of Site‐Specific Osteoarthritis From 1990 to 2019 : Findings From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Arthritis & Rheumatology, 74(7), 11721183. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.42089
- Amoako AO, Pu–jalte GG. Osteoarthritis in young, active, and athletic individuals. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;7:27-32. Published 2014 May 22. doi:10.4137/CMAMD.S14386
- Cui A, Li H, Wang D, Zhong J, Chen Y, Lu H. Global, regional prevalence, incidence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in population-based studies. EClinicalMedicine. 2020;29-30:100587. Published 2020 Nov 26. doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100587
- Ziltener, J., Leal, S., & Borloz, S. (2012c, mars 14). Activités physiques – sport et arthrose. Revue Medicale Suisse. https://www.revmed.ch/revue-medicale-suisse/2012/revue-medicale-suisse-332/activites-physiques-sport-et-arthrose
- Fernández-Moreno M, Rego I, Carreira-Garcia V, Blanco FJ. Genetics in osteoarthritis. Curr Genomics. 2008;9(8):542-547. doi:10.2174/138920208786847953
- Widhalm HK & al. Osteoarthritis in morbidly obese children and adolescents, an age-matched controlled study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016 Mar;24(3):644-52. doi: 10.1007/s00167-014-3068-4. Epub 2014 May 20. PMID: 24841943.
- Khan M, Adili A, Winemaker M, Bhandari M. Management of osteoarthritis of the knee in younger patients. CMAJ. 2018;190(3):E72-E79. doi:10.1503/cmaj.170696
- London NJ, Miller LE, Block JE. Clinical and economic consequences of the treatment gap in knee osteoarthritis management. Med Hypotheses. 2011 Jun;76(6):887-92. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2011.02.044. Epub 2011 Mar 25. PMID: 21440373.


