What is foot drop?

What is foot drop syndrome?
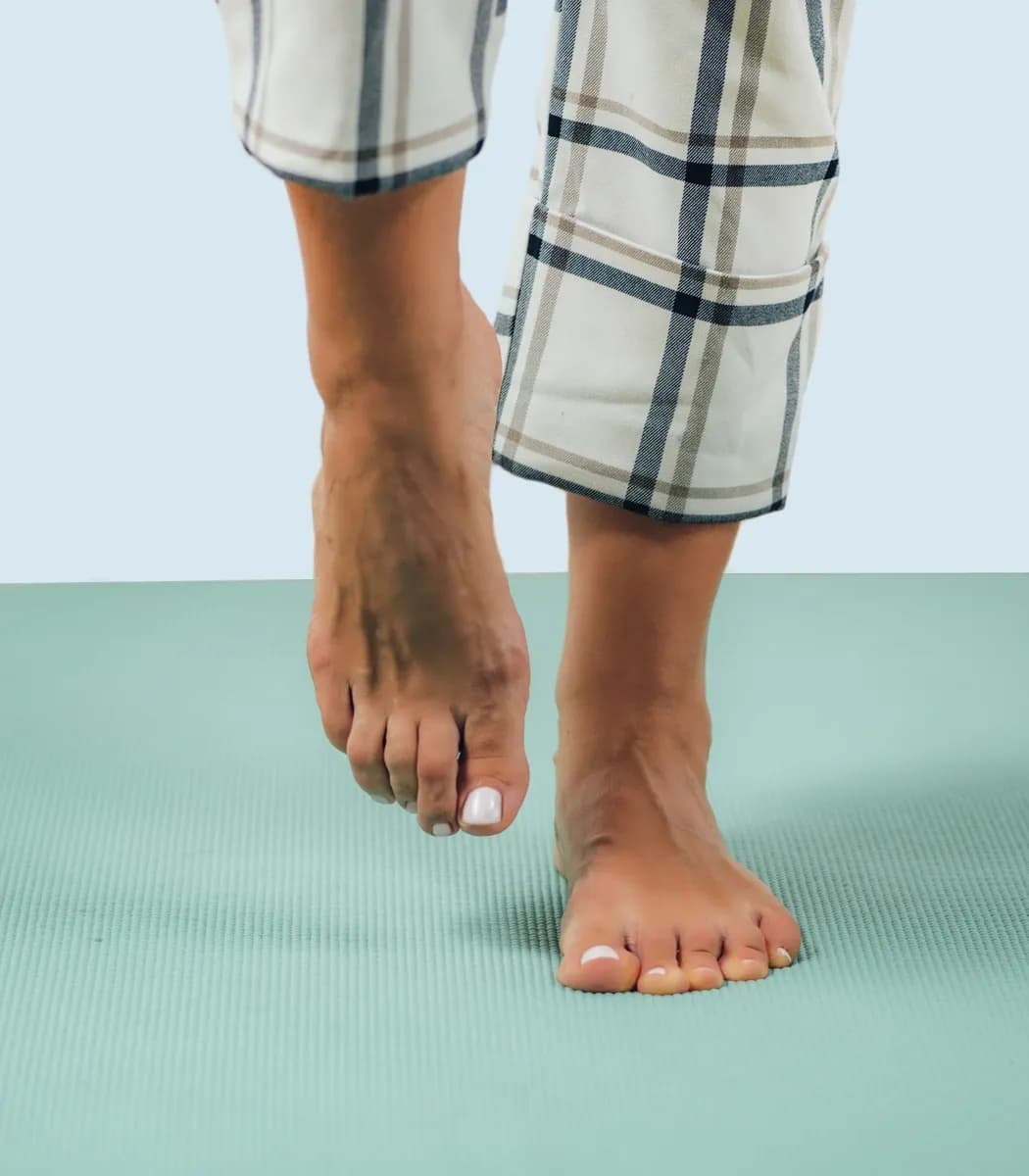
Foot drop, also known as steppage, is a symptom that affects the mobility of the foot. A sufferer experiences difficulty, or even an inability, to lift their foot when walking due to abnormal weakness in the lower limbs. As a result, the foot systematically points towards the ground and is difficult (if not impossible) to lift(3).
It is not a disease, but a symptom often caused by neurodegenerative disorders of the brain (such as multiple sclerosis, stroke and cerebral palsy), compression or local lesion of the peroneal nerve and muscular disorders (such as muscular dystrophy or myositis)... and can affect anyone temporarily or permanently(3).

What causes foot drop?
Foot drop or steppage is not a disease. It is the result of weakness or paralysis of the muscles that lift the front part of the foot (foot-lifting muscles). It may be the result of a variety of pathologies or traumatic events (2,3).
Nervous system dysfunction
Nerve damage linked to diabetes, known as neuropathy, can lead to difficulty or even inability to lift the foot(4).
Hereditary disorders such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy) can also cause the foot to fall off(3).
Conditions affecting the brain or spinal cord, such as: stroke (ischaemia of brain tissue and necrosis or compression); cerebral palsy (perinatal brain damage); multiple sclerosis (attack by the immune system of the myelin surrounding nerve fibres)(3).
Nerves in the leg may also be injured or damaged during joint replacement surgery.
Foot drop is also often caused by crushing (compression) of the nerve that controls the muscles that lift the foot, the nerves around the knee or the nerves in the lower spine.
Muscular system dysfunction
Muscle disorders, such as muscular dystrophy or myositis, cause progressive muscle weakness and can lead to foot drop, among other things(3,5).
Foot drop can also result from direct trauma, such as fibular fractures or knee dislocations, or from neuromuscular diseases such as focal myopathies or multifocal motor neuropathy(6).
How can I live with a foot drop?
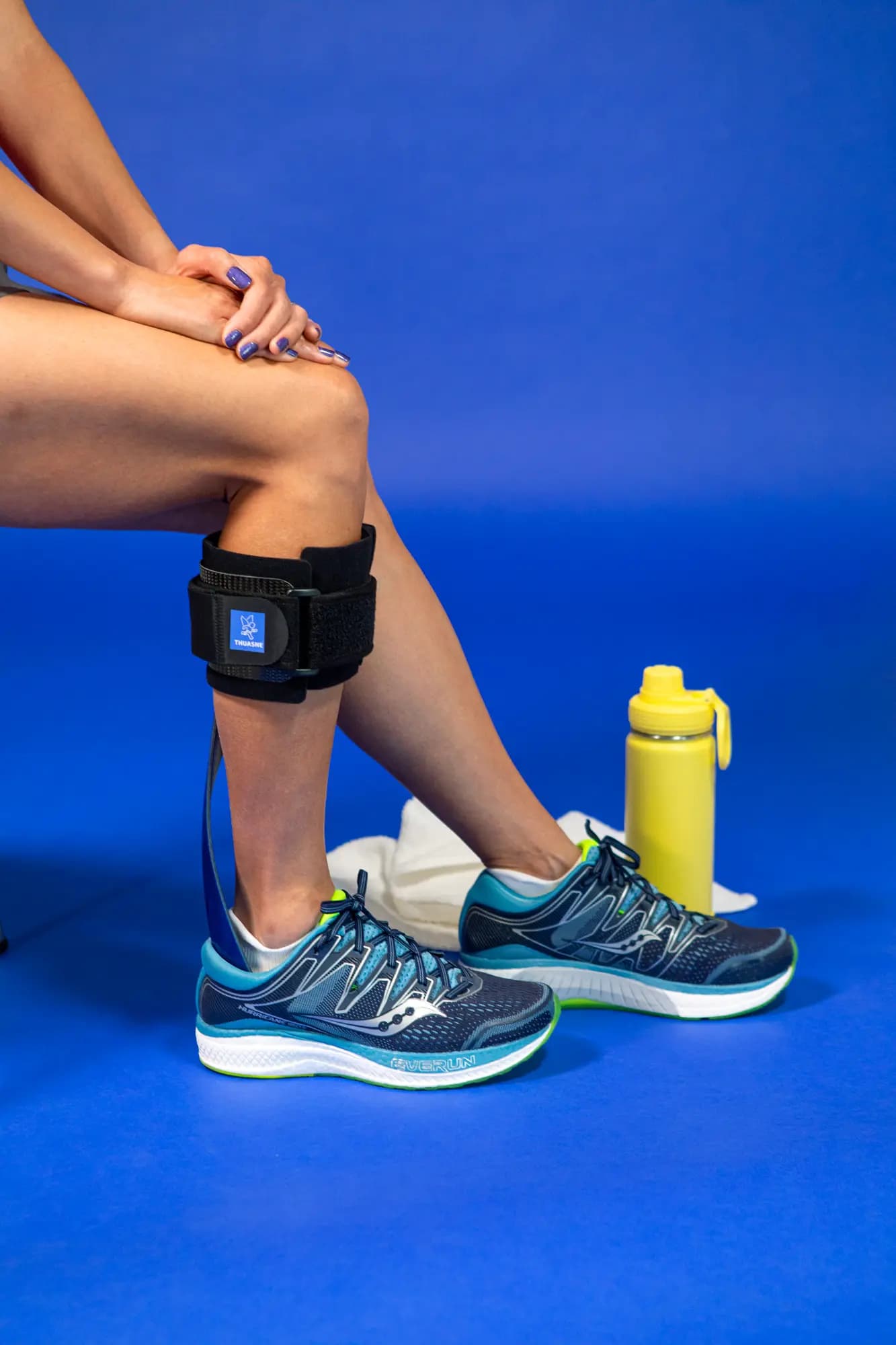
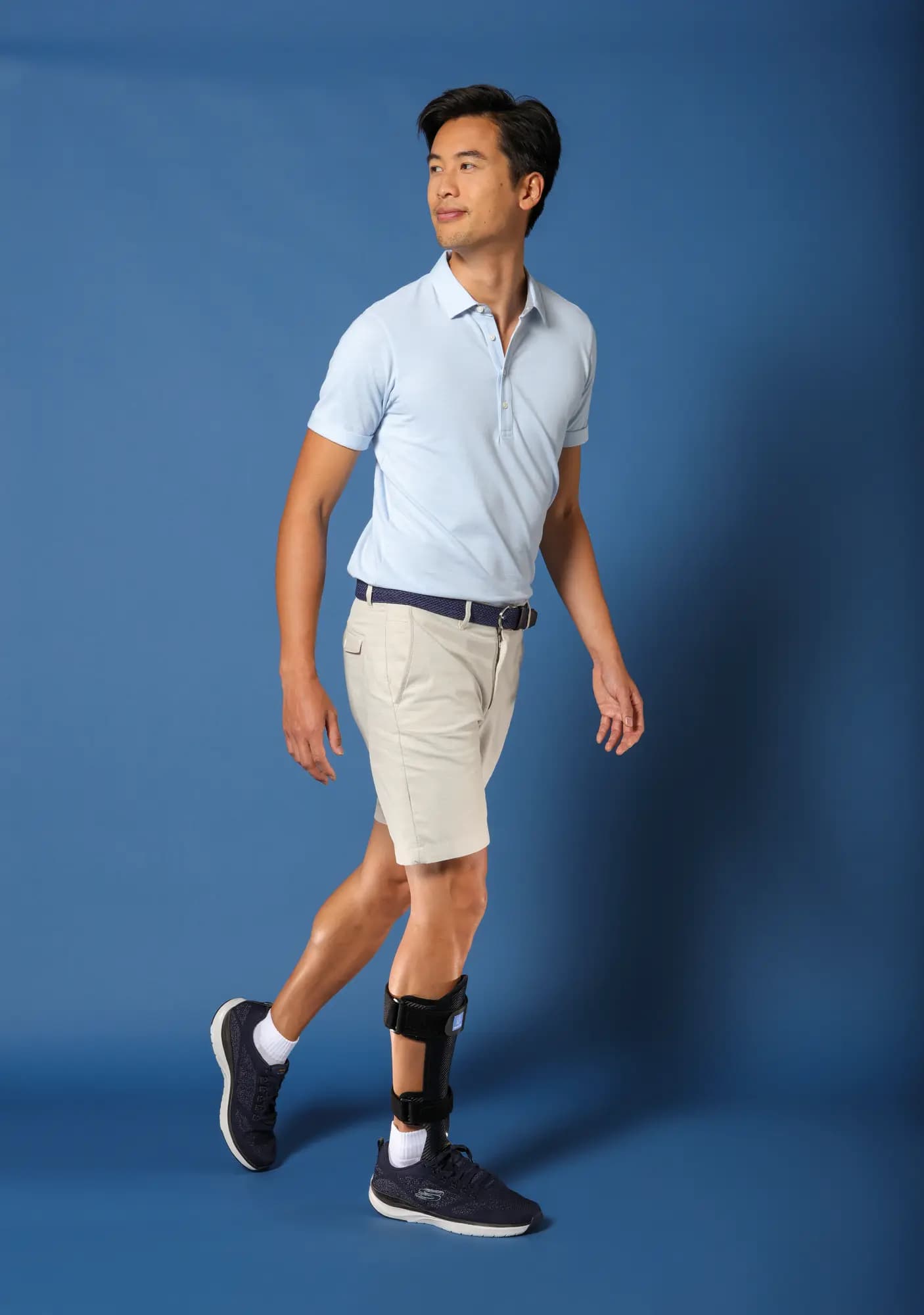
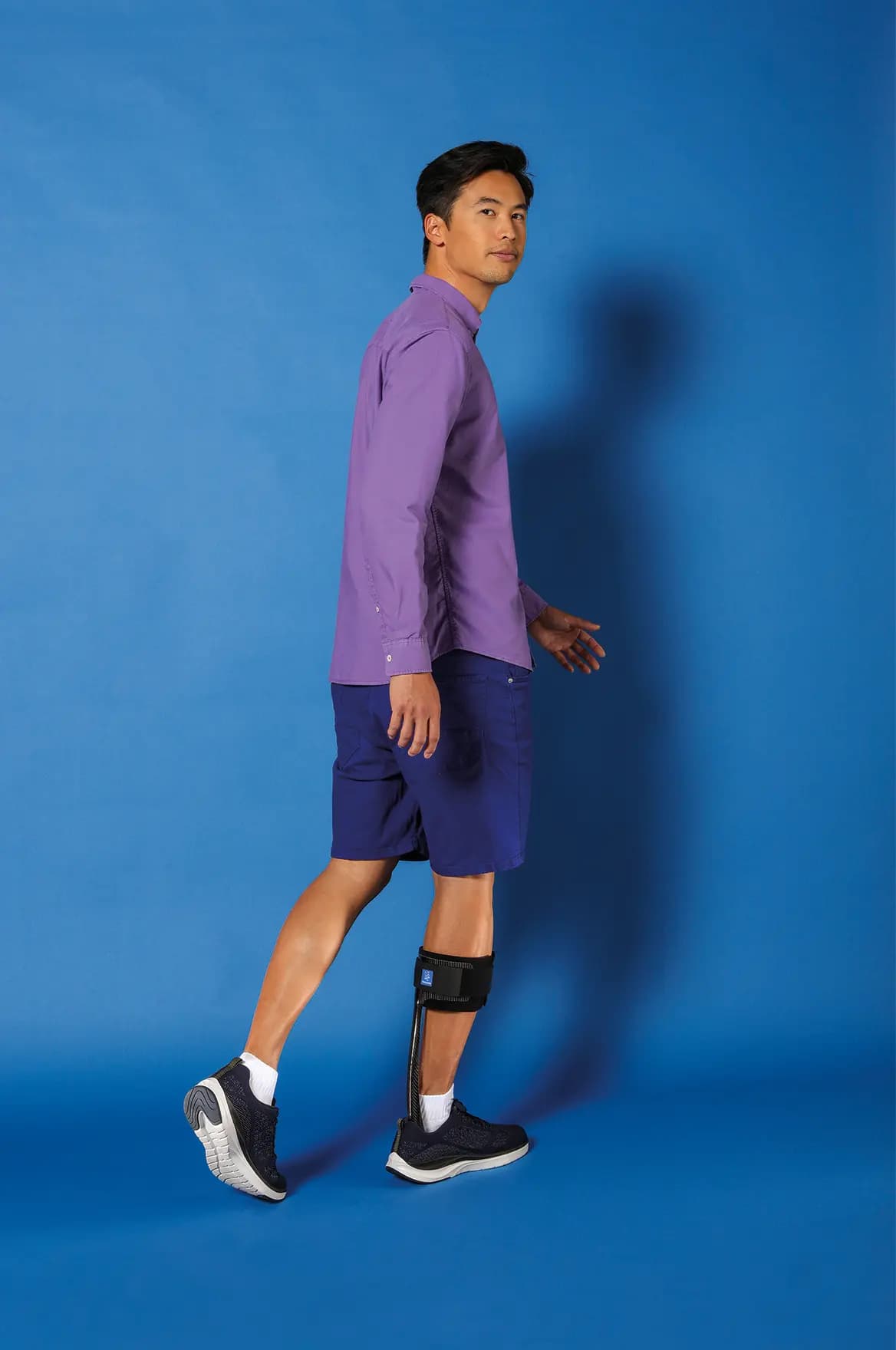
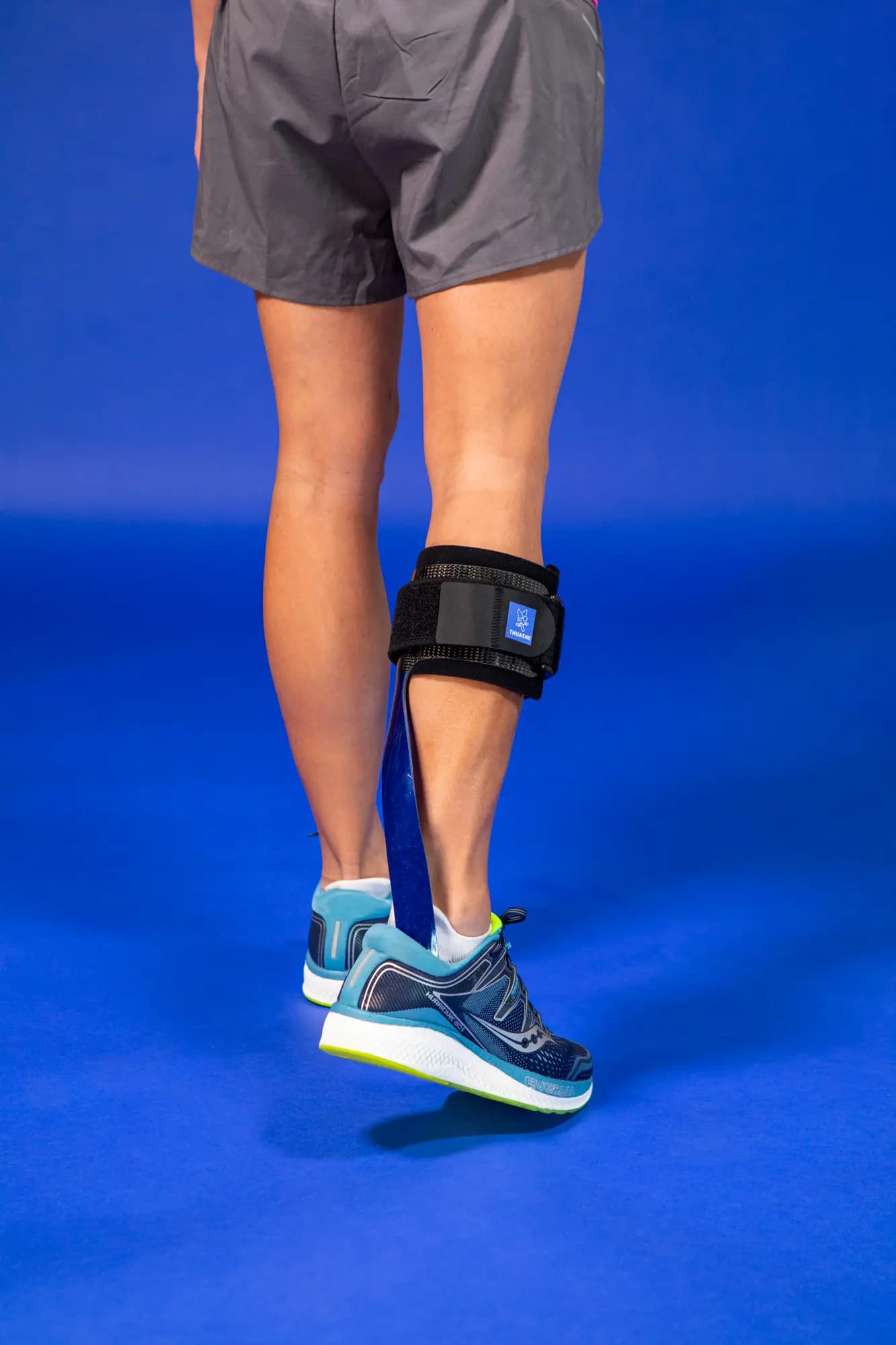
A foot lifter for safer walking
A foot lifter is an orthopaedic device (also called an orthosis or splint) that helps people with foot drop to keep their foot at an appropriate angle to help improve foot clearance and safety when walking. Foot lifts can also be used to control ankle rotation and knee positioning according to the patient's needs.
Why wear an orthosis?
When you suffer from steppage, it means that the muscles responsible for flexing the foot (also known as the foot-lifter muscles) and/or the leg muscles no longer play their role. As a result, the mobility of the foot is greatly affected and a person suffering from this condition finds it difficult or even impossible to lift their foot when walking, as it systematically points towards the ground and is difficult (if not impossible) to lift.
Fitting a foot lift is a non-invasive, non-pharmacological solution that compensates for dysfunction of the foot lift muscles and supports leg movement to improve walking(6,7). Thuasne® supports you by offering foot lifts adapted to your needs. Consult a healthcare professional before fitting any orthopaedic devices.
To find out more about how an orthotic can help you live with foot drop syndrome, read our article.

What are the treatments for foot drop?
Treatment for foot drop will depend on the cause of the symptom, whether neurological, muscular or traumatic. Whatever the treatment, the aim remains the same: to enable the patient to regain maximum mobility and help them to lift their foot. Here's what we can suggest:
Exercises for foot drop
Initially carried out with the help of a healthcare professional (a physiotherapist, for example), these help to strengthen the leg muscles in order to improve walking movement(6).
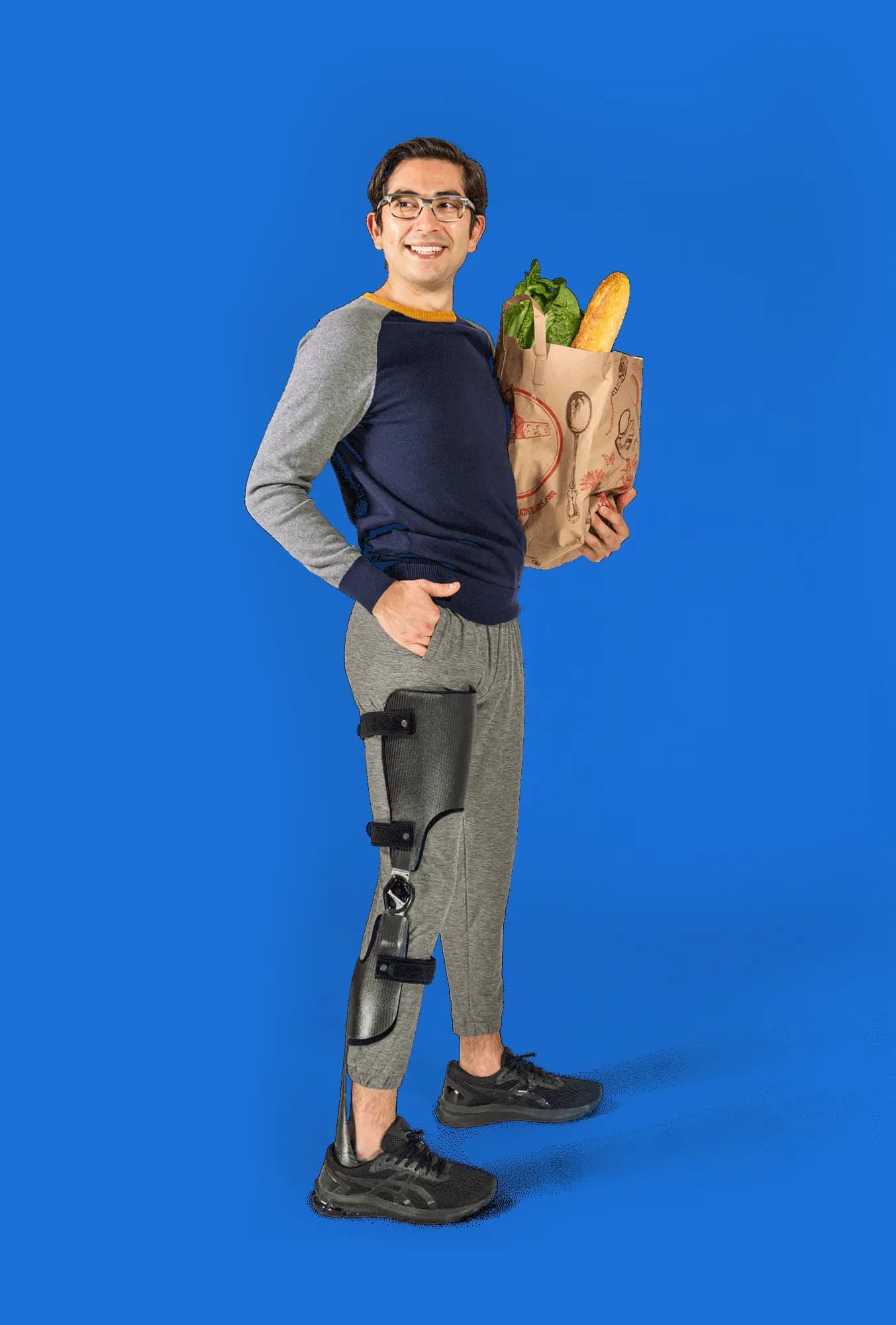
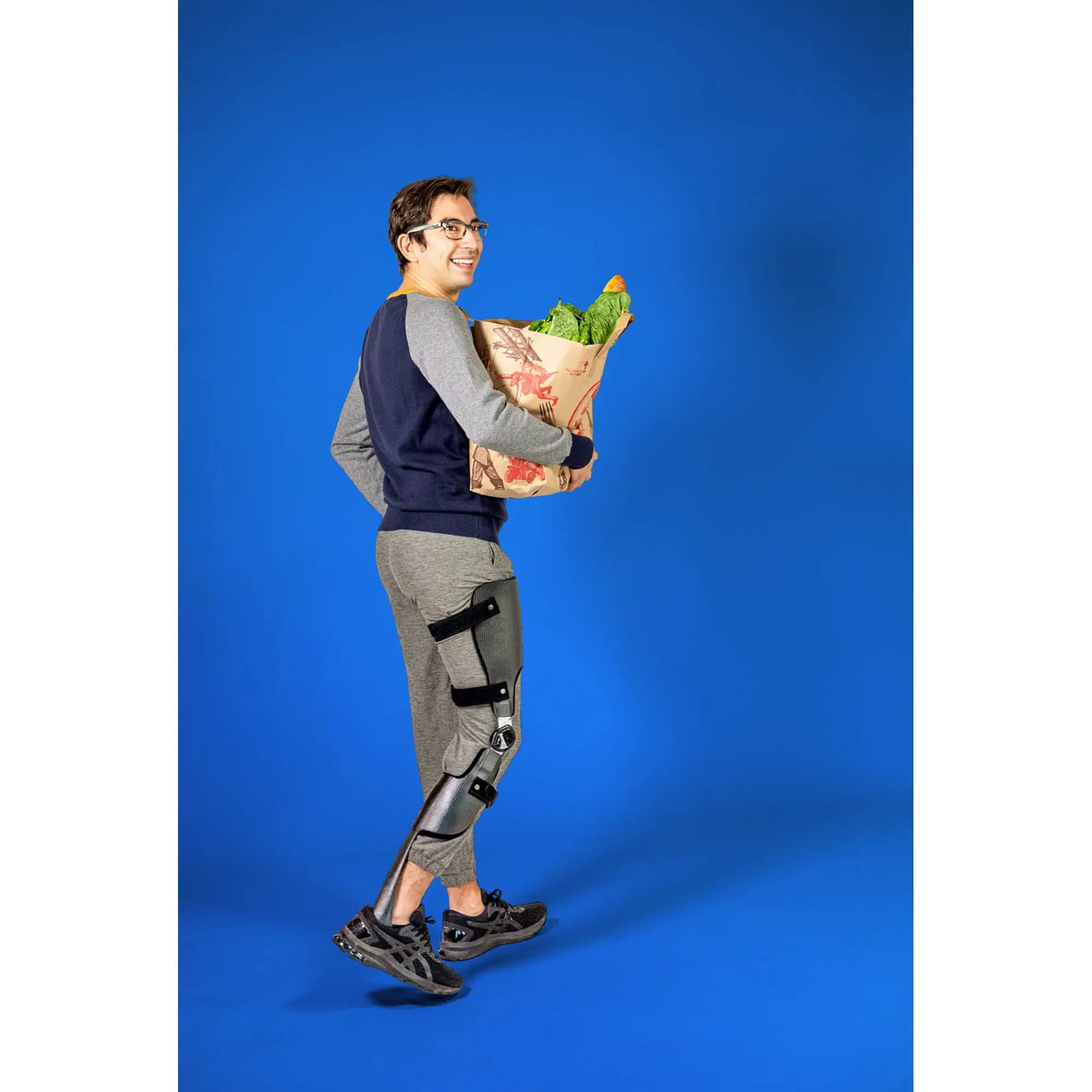
Orthopaedic devices
Such as the foot lifter - or knee-ankle-foot orthosis (cruro-pedis) - is positioned in or on the shoe and lifts the foot that is drooping. It allows more natural walking and improves balance(6,7).
Nerve stimulation
Nerve stimulation is a rehabilitation technique that involves applying electrical currents to peripheral nerves to improve the movement or function of organs, muscles and limbs(8).
Surgery for foot drop
Surgery may be an alternative in some cases, to repair muscles or tendons or decompress the pinched nerve(6).
Only a healthcare professional will be able to advise on the most appropriate treatment.

FAQ about foot drop
Our medical team answers the questions you may have.
If you suffer from foot drop syndrome, your physiotherapist will probably advise you to do some exercises to help you strengthen your leg muscles and improve your walking. Some exercises will help you lift your foot, rotate your foot and walk on your heels. But don't do any exercises without consulting a health professional.
If you suspect you have a foot drop, several healthcare professionals can be consulted.
- A general practitioner may be the first point of contact, and will be able to refer you to a specialist if necessary.
- A neurologist is often consulted to identify a possible neurological origin of the symptom.
- An orthopaedist may be called in to assess a muscular or bone-related cause.
- A podiatrist or chiropodist specialising in foot disorders may also be a good option.
- Finally, a physiotherapist is often involved as part of the treatment plan to help improve mobility and strength in the leg.
The advantage with SpryStep® products is that you can cut the sole to fit the width of your shoes. This makes the orthosis adaptable to many closed shoes.
Foot drop syndrome is an indicative symptom of an underlying problem and can be temporary or permanent, depending on the cause. Possible causes include neurodegenerative disorders of the brain, muscle disorders, and compression or local injury of the peroneal nerve. Early surgical intervention generally tends to improve outcomes, as demonstrated by the example of foot drop caused by lumbar degenerative disease(9).
- « (Goldner, J., & Thomas, J. (2019). Foot drop.. GP, 40 1, 89-96 . https://doi.org/10.32388/863841. )
- Des muscles du membre inférieur, provenant d’une diminution de la force musculaire (Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. 3rd edition, John Holbrook 1990)
- Corcillo A, Kleinaki Z, Kapnisi S, Fountoulakis N, Maltese G, Thomas SM, Karalliedde J. Painless foot drop: an unusual acute presentation of new onset type 1 diabetes mellitus. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2021 Mar 16;2021:21-0012. doi: 10.1530/EDM-21-0012. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33845454; PMCID: PMC7983474.
- Roy B, Dimachkie MM, Naddaf E. Phenotypic spectrum of inclusion body myositis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2024 Feb;42(2):445-453. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/fhrx3q. Epub 2024 Feb 28. PMID: 38436356.
- Carolus AE, Becker M, Cuny J, Smektala R, Schmieder K, Brenke C. The Interdisciplinary Management of Foot Drop. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019 May 17;116(20):347-354. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0347. PMID: 31288916; PMCID: PMC6637663.
- Daryabor, A., Kobayashi, T., Yamamoto, S., Lyons, S. M., Orendurff, M., & Akbarzadeh Baghban, A. (2021). Effect of ankle-foot orthoses on functional outcome measurements in individuals with stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Disability and Rehabilitation, 44(22), 6566–6581. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638288.2021.1970248
- Ho C, Adcock L. Foot Drop Stimulators for Foot Drop: A Review of Clinical, Cost-Effectiveness, and Guidelines [Internet]. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2018 Nov 21. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537874/
- Berger, A., Mangel, L., Basal, S., Lidar, Z., Regev, G. J., Khashan, M., Ofir, D., & Salame, K. (2022). Predictors of functional recovery following surgery for foot drop due to degenerative lumbar disease. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine, 36(3), 408-413. https://doi.org/10.3171/2021.5.SPINE21350